Osteochondral Lesions
Ligament injuries are not the most dangerous consequences of an ankle sprain.
The most dangerous are cartilage lesions: osteochondral lesions.
In fact, articular cartilage can be damaged due to the impact of the distortion itself. The articular surface that is likely to be more susceptible to this type of injury is that of the talus due to the impact with the surface of the tibia, an overlying bone segment.
Sometimes, but more rarely, “kissing lesions” can be found, which are matching lesions that involve both the talus and the tibial articular surface.
The danger of these injuries derives from the high risk of chronicity. Cartilage has no regenerative power. This means that our body tries to replace the damaged cartilaginous tissue with fibrous tissue, which obviously does not have the same characteristics and is not able to perform the same functions.
TopNext
CAT Scan
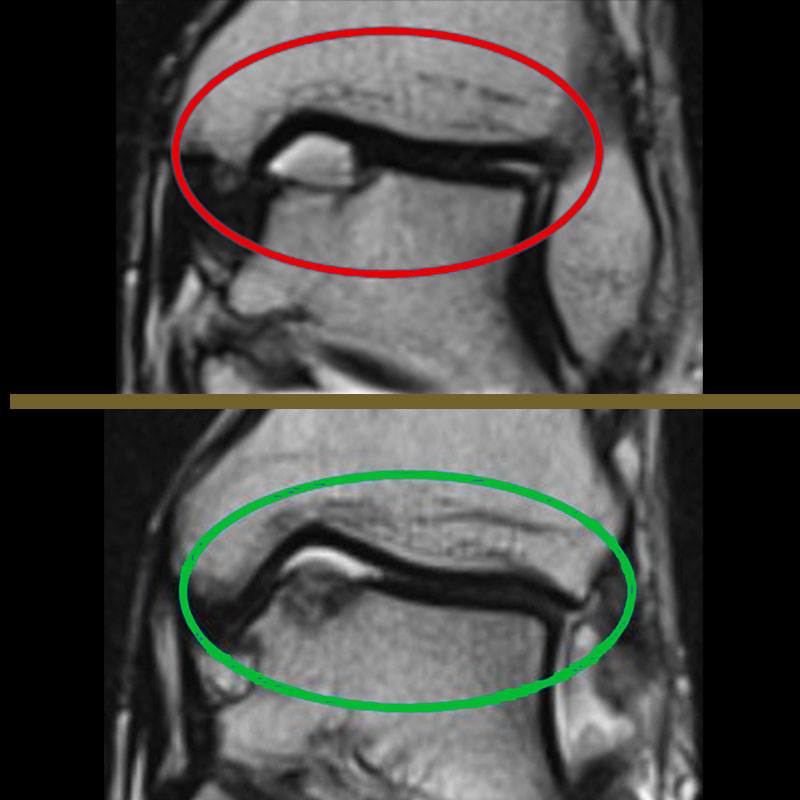
The CAT scan helps us, in an even more precise way than the MRI, outline the margins of the osteochondral lesion to understand its real dimensions and depth.
Both of these tests are essential for correct surgical planning in case of an osteochondral lesion.
TopNext
Surgery for Osteochondral Lesions
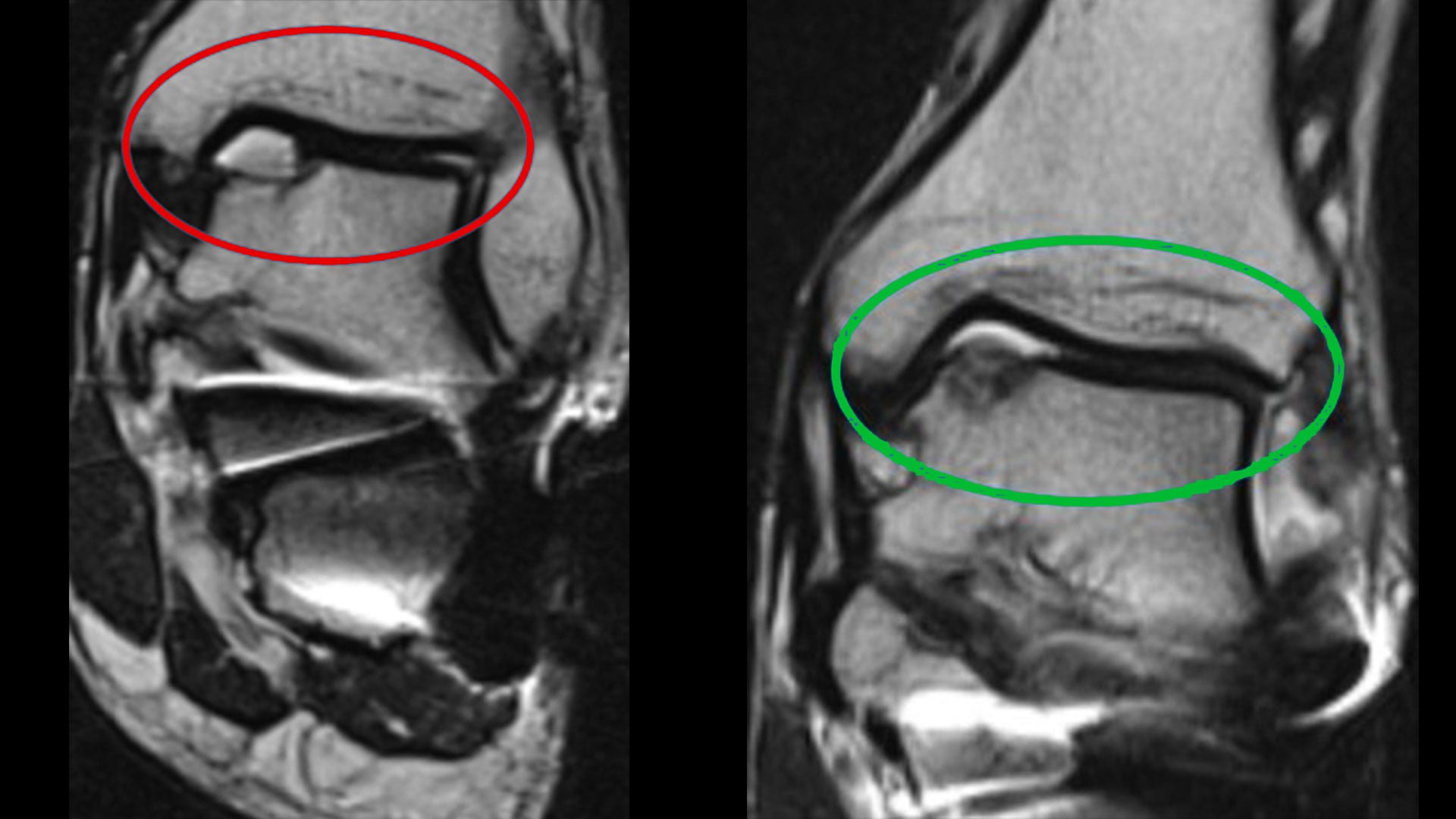
The surgical technique we designed and published in international scientific journals is called AT-AMIC.
This is to be taken into consideration for osteochondral lesions (articular cartilage) and is aimed at its repair.
It provides an arthroscopic approach through which, with minimal invasiveness, a cartilaginous reconstruction is allowed by using the biological potential of the organism through nano-perforations that induce the escape of “mesenchymal” cells on the surface.
However, these nano-perforations alone are not sufficient to promote correct regeneration. In fact, without a “guide” they would tend to crowd the area of the lesions in a disorderly way, not leading to correct tissue regeneration.
This is the role of the biological membrane we use. This collagen membrane, which is always introduced through arthroscopic access, behaves like a real network, which allows each cell to find its right location, allowing the regeneration of a tissue with characteristics close to those of the original cartilage.
Obviously the isolated cartilaginous repair, in the case that there are other pathological factors, is not sufficient to solve the problem. This is why, if an ankle sprain causes a cartilage damage associated with a ligamentous lesion capable of giving instability, both must be repaired: cartilage and ligaments.
Equally important is to evaluate the alignment and eventual overload weight pressure that may expose the cartilage repair to risks of recurrence.
In these cases, consideration should be given to the possibility of acting at the bone segment level with corrective osteotomies. These types of surgeries, which lose the characteristic of being minimally invasive, are absolutely necessary in case of misalignments, which would lead to the failure of the only biological reconstruction.
TopNext
Recovery Time


In the case of a surgery aimed at cartilaginous reconstruction, the post-operative period includes two days in the hospital after which one is discharged with a bandage and with the advice of limiting the movements of the ankle as much as possible to prevent biological membrane mobilization.
On the 15th day, physiotherapy and water gymnastics (hydrotherapy) will begin to recover confidence with the weight of the standing position.
Full standing recovery begins gradually from the fourth week. The patient can be satisfied about 6 months after the surgery, keeping in mind that, thanks to the biological process of repair that continues over time, one can have a continuous though slow improvement up to at least 1 year after the surgery itself.
Some examples: permission to drive will be granted after 4 weeks; a cautious and gradual resumption of running on regular terrain will normally be possible 3 months after the surgery; high-stress sports activities for the ankle will be possible after 6 months.
It is important to consider that the symptoms related to the disease will no longer be recognized only three weeks after the surgery, but given the presence of continuous reparative phenomena, monitored with MRIs, the priority is to avoid mechanical stress that may compromise the quality of cartilage repair.
In necessary cases, in addition to the cartilage repair surgeries, there must also be skeletal realignment by performing osteotomies, post-operation involves the use of an ankle cast for 4 weeks on which weight is not allowed.
When the cast is removed the patient will have to perform independent hydrotherapy and gradually return to carrying out his daily activities. Sporting activity must be postponed to 4-5 months after surgery.
TopNext
My Team’s Research on Ankle Instability
My group’s work has led to a new technique of completely arthroscopic cartilage regeneration and to the analysis of the results obtainable with this technique, opening new therapeutic scenarios for young and younger patients, for overweight and non-overweight patients, and for high level athletes and individuals with normal physical activity.
Today, our AT-Amic is considered one of the techniques of choice for cartilage repair and one of the scientific topics most written about in the field concerning cartilage and ankle.